Photo by Jess Bailey on Unsplash
The Covid-19 pandemic has disrupted people’s daily routines. Want to grab that favorite cup of coffee down the street? Sorry, the coffee shop is closed. Spaghetti and meatball night? Too bad, the local store ran out of ground beef. Client meeting at the office? Nope, Zoom meeting with surprise appearance of adorable kids or pets is the way to go now.
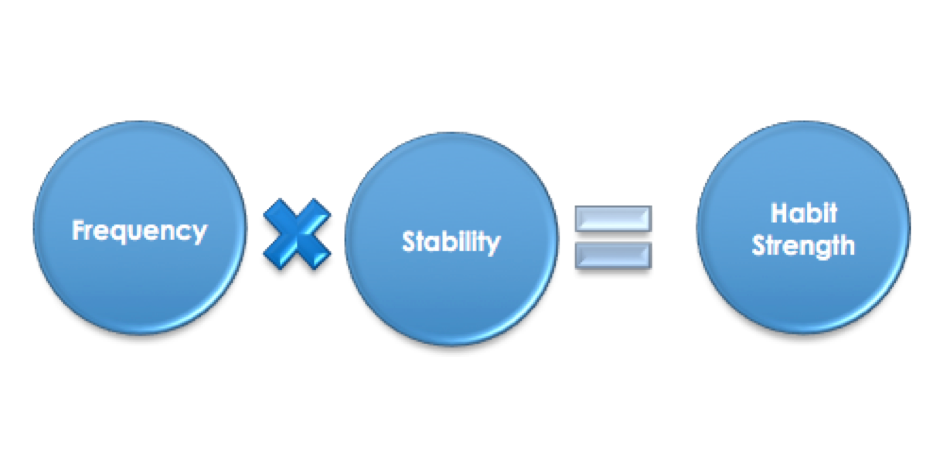
In these and many other areas of life, the well-rehearsed habits people had from the “old” days are suddenly thrust into the spotlight of their consciousness. As a result, old habits are breaking, and in their place new habits sprout. These transformations in habits have significant consequences for business. Some brands are being left behind from broken old habits, while others are discovering opportunities among the new habits. Overall, businesses that understand this habit transformation process about their customers will be better prepared to transition through the pandemic and beyond.
This article looks into psychology research to shed light on the habit transformation process and discusses how customer relationship management should respond to such disruptions.
Continue reading “CRM in an Era of Habit Disruption”